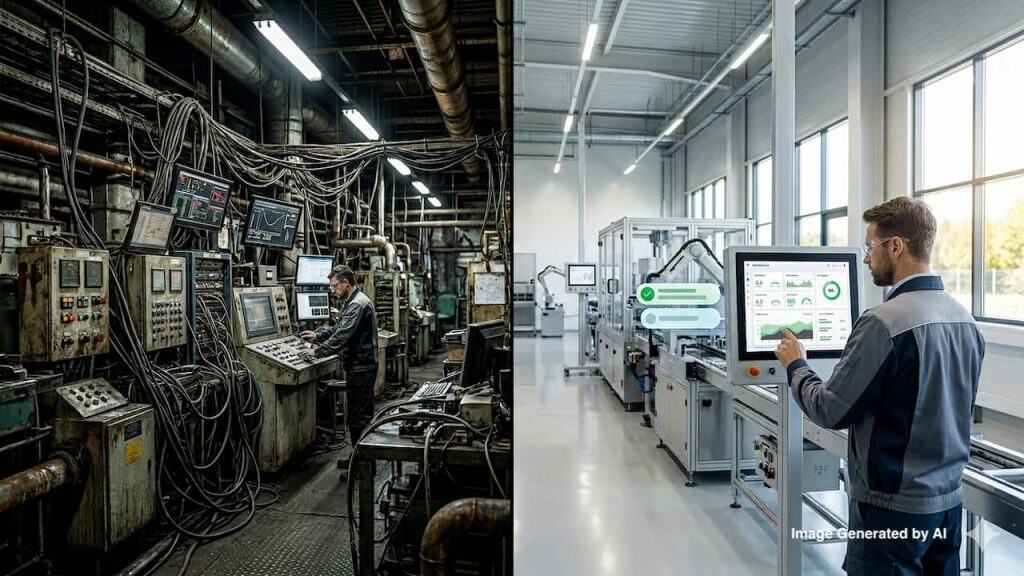
Science and technology are essential tools for innovation. In the next few years, the impact of Digital Transformation will accelerate. Internet of Things (IoT aka M2M, IIOT, IoE – though each has its specific focus) is considered the most important trend in digitization.
From connected homes, cars, cities to entire industries such as healthcare, insurance, manufacturing, public sector and utilities – connected and increasingly intelligent devices are transforming entire ecosystems, and one of the components are robots. Today, in our first Robotics Q&A, Mauro Fenzi, the CEO of Comau, discusses about different types of robots that already have a huge impact on manufacturing and other industries.
Lucian Fogoros: It’s been over 50 years since the first industrial robot went to work. Can you talk about the changes in the industry?
Mauro Fenzi: The industry is experiencing a new, deep change thanks to the so called Fourth Industrial Revolution. The Industry 4.0 developments are progressively digitalizing the manufacturing system, leading to significant changes which require companies to have increasingly flexible production processes, producing in small batches, with high customization and a reduced time-to-market without compromising high technical performance.
This change involves both multinational companies and SMEs in different ways and times, depending also on the countries. For this reason, Comau, a company part of the FCA Group, is guiding companies – of all sizes – in this process, providing them with customized solutions and, above all, easy-to-use solutions for factory automation. Our objective is to reduce the entry barriers to the use of industrial automation solutions, making the use of digital products and technologies easier. This is why, for instance, we have been experimenting on intuitive and easy to use tools for production lines in an IoT view.
Lucian Fogoros: Around the world, robots are performing difficult, dirty and sometime dangerous tasks. Robots are flexible, they are not adaptable yet (Adaptable would mean that if a part arrived upside down the robot could recognize this and correct it.) How soon will AI change this situation with mainstream adoption?
Mauro Fenzi: Industry 4.0 is redefining the roles of automated machinery and man in a collaborative context. Over the years, automation has improved working conditions, allowing people to deal less with heavy, tiring and dangerous tasks and giving them a superior position in the process, all while increasing their efficiency, productivity and the quality of the final result. Now, technological developments have enabled man to be working close to machines in complete safety, in a smart way, improving plant productivity and working conditions for operators.
To demonstrate how this new way of working in the industrial sector is possible, Comau has launched a new collaborative robot called AURA – Advanced Use Robotic Arm – an innovative product for the robotics industry that, for the first time, creates a true collaboration between high payload robots and man on a production line. AURA is inspired by human interactions and the use of human senses: for the first time, a robot can combine the simultaneous perception of the proximity of a person – or of any other component of automation – as well as their contact and their intensity. This is possible because AURA is equipped with sensors installed under a layer of protective foam to ensure total safety. The combined use of this technology, united to laser scanners to identify the positions of people, makes it possible to ramp down the motion of the robot to a complete stop only when it is very close to or actually in contact with the worker.
Comau is redefining the vision of the smart factory, not only in the context of collaborative robotics. We are developing, for example, supporting HMI applications for operators in managing the assembly and maintenance operations through the use of some apps to use on smartwatches, smartphones, tablets, to improve the activities of operators in a production line. We are engaged in developing new mobile platforms to autonomous driving, including modular and wide-ranging solutions, for logistics applications in the operator’s support production systems.
To maximize efficiency, productivity and the quality of working in manufacturing plants, Comau, in partnership with the company Engineering, has developed a new project, called Digital Workplace. DIWO Suite is the result of a joint development of an application framework, based on best-in-class technology platforms, for the collection and analysis of field data to predict and anticipate potential malfunctioning of machines and tools and the negative trends in the quality of the manufacturing processes. To allow its complete and integrated use in a factory, DIWO Suite is composed of 4 modules: DIWO Virtual Plant, to virtualize the shop floor by enabling read/write operations and event notification; DIWO Maps, to enable performing real-time monitoring and analysis of production lines/units behavior; DIWO HMI, to enable using manufacturing applications in an easier way all over the plants and DIWO Analytics, to enable taking advantage of open standards for Big Data & Analytics.
Finally, during the Hannover Messe, we presented to the market a new smart robotic solution: e.DO, a unique, “build-it-yourself” 6-axis articulated robot, based on a 100% open-source hardware and software platform. e.DO is perfect for educational, professional, entertainment, and consumer use, and can also be leveraged by expert users to drive real-world business applications. Once configured, e.DO can handle a wide range of tasks – from simple pick and place movements to performing tasks and acting as an automated guided vehicle. As an open-source project, e.DO has a hardware and software structure designed to encourage application sharing and expansion via the growing e.DO community.
Lucian Fogoros: What industries are best suited to robotic automation? Why?
Mauro Fenzi: Robotic automation is traditionally best suited for the automotive industry, where the extensive production of highly advanced technological products requires the speed, precision, repeatability and endurance only machines can deliver. However, robots are a strategic solution also for the general industry, being suitable to be applied, for example, in electronics, as well as packaging or foundry, food and beverage, white goods, bio medical and many more sectors where they can easily carry out repetitive, dangerous and difficult tasks. Brand new markets are emerging for robotics and, generally, industrial automation, such as the entertainment industry.
Lucian Fogoros: What robotic technology do you see gaining the most traction in manufacturing industry in the near future?
Mauro Fenzi: Collaborative robotics. In Comau’s vision, Industry 4.0 is characterized by the direct collaboration between man and machine, a concept we define as “HUMANufacturing”. This concept may prove to be even more surprising when developed by a company that manufactures industrial robots. The reason why we call it “HUMANufacturing” is that, for the first time, industrial robots are no longer confined within the barriers that enclose their area of use. In fact, they now work alongside the operators, directly inside the production line.
Lucian Fogoros: What is the biggest trend our readers can look forward to in the robotics market in the next year?
Mauro Fenzi: We can identify two major trends: integration and education.
On one side, by integration we mean bringing together the different competencies of companies and corporations in industrial automation. This allows – and always will allow more in the future – to deal more easily and innovatively with all the new digital industry needs, creating new and challenging projects.
A significant example of this, is the network Comau created with global cooperation agreements signed recently, e.g. with Ericsson to test the use of 5G technologies in the factory.
On the other side, companies will increasingly need to rely on people who can effectively use all tools and typical enabling technologies of the digital revolution such as additive manufacturing, augmented reality, cloud, big data and cyber security. The ‘digital employee’ requires new skills, and this is why Comau, through the activities of its Academy, is committed to the development of technical and managerial skills of their employees, but also to university students and recent graduates who want to train in the field of industrial automation and digitization. We do so working together with major institutions and universities worldwide such as the BioRobotics Institute – Scuola Superiore Sant’Anna and the Politecnico of Turin. In terms of Comau Academy, we have just launched, in collaboration with ESCP Europe, one of the oldest and most prestigious business schools, a new Executive Master in “Manufacturing Automation & Digital Transformation” in order to develop the skills necessary to design and manage more innovative industrial automation solutions and in step with market demands. The course of study – developed together with the Politecnico of Milan and the Technische Universität of Munich – will be held in three different countries, Germany, Great Britain and Italy.