Enabling Manufacturing using IOTA – A possible approach post Covid-19 paradigm
Internet of Things is no more a technological breakthrough. Industrial applications have been faster in adoption of IoT and it has been playing a significant role for businesses that requires internal tracking, attaining near to zero error with less manual intervention, enabling machine to machine talking along with prognostic maintenance. RFID chips and other sensors are much cheaper in terms of cost and easier to manufacture than most of the sizeable and lumbering consumer electronics. The future of IoT will continue in these lines, especially post COVID with lot of manufacturing concerns embracing automation at a massive scale gradually shaping the smart industrial applications concept.
However, the blockchain of IoT also calls for distributed and secure exchange of data captured through these sensors or devices. The interconnection of blockchain technology and IoT have been in the scenario since 2015, to solve critical IoT challenges related to security and data privacy. The IOTA protocol has been able to enter into collaborations which technically differentiates itself from most of the cryptocurrencies by its underlying technology that uses Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) as a distributed ledger which stores the transactional data of the IOTA network, instead of blockchain enabled transactions. This proposed system uses IOTA’s ledger, called Tangle – a database to store the data that it aggregates by issuing transactions.
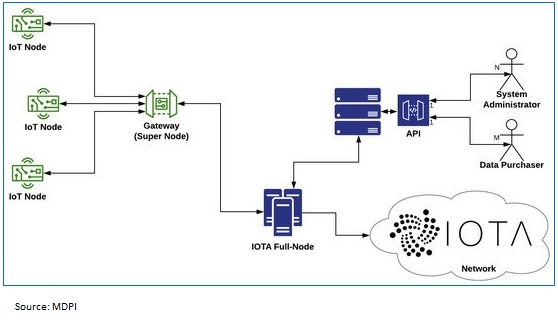
IOTA Over Blockchain – Leveraging the technology
- The Transaction Rate – Blockchain has a very low transaction rate while the rate of transaction in IOTA is significantly higher due to more users and shorter time required for transaction approval.
- Efficiency of the tech – Since the mining process is shortened in IOTA, the efficiency in terms of computing power is much higher, also the electricity consumption is less as compared to blockchain technology
- The Security Compliance – Though the blockchain can be prevented from external manipulation, there stands a risk of internal data manipulation in order to increase the transaction rate. Since the latency of the IOTA is quite low the transaction happens between the enterprise system and a trusted instance.
- Scalability – With increase in users and the transactions, the system gets much faster. Moreover, the latency is also much low that enables the scaling of the system.
Hence, it is of utmost interest to the industry as the Tangle technology in the IOTA network replaces the minors with the creators of transactions who perform Proofs of Work (PoW) computation on behalf of the user. Thus, companies can adapt Tangle to support their use cases, integrate payment process, document transactions all at the same time in addition to being legally compliant.
The Post Covid-19 Paradigm at the Industrial Front
While the world is gripped by the Covid-19 pandemic the global supply chain and manufacturing falters, experiencing a new level of disruption. While lot of the manufacturers have ceased production, some are experiencing a record low demand. A lot many have also addressed a sudden surge in demand. This uncertainty poses an existential threat. Industrial equipment is one of the sub-sectors that are grappling with the impact of the pandemic. Research indicates the industrial equipment industry represents 25% of global manufacturing GDP (Comprising 21% in US, 25.4% in Europe and 32.9% in Japan). Thus, industrial equipment manufacturing is one section of the sector that needs the preparedness for ramping back of their operations post Covid-19. The priorities for most manufacturers can be explicitly classified into a simple model of Business as Usual, Sustenance and Regrowth.
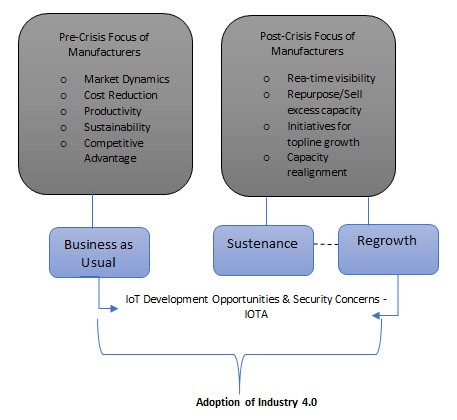
The goal for manufacturers Post-Crisis would be to attain the Regrowth Phase. To curate up, some fundamental questions addressing the weaknesses, costly decisions and what would have helped in [the business continuity might help in key findings of the systems and processes. While Industry 4.0 was already being implemented in the Business as Usual Phase, it’s the leapfrogging to Regrowth that would require a robust framework comprising more of IoT adoption. Though it’s early to say anything amidst all the uncertainties but real-time visibility across the business and capacity realignment is what grabs the industry attention. With global operations relying on international supply chains which are currently distorted, few of the anticipated changes to the industry that the manufacturers would have to adjust to:
- A digitally enabled workplace and reskilling of workforce
- Establishing a centralized system for faster response deployment
- Resilient supply chains by customer segment
- Establish cost reduction initiatives for medium- and long-term impacts for business
- Future Scalability across the value chain
- Momentum on ongoing operation capability and security concerns
- Better demand forecasting
Implication of IOTA – Looking at the aforesaid issues
- Supply chain with many stakeholders or actors can gauge real-time visibility by using the IOTA tangle and Masked Authenticated Protocol (MAM), where different stakeholders can have different access privileges
- All transactions, events and data are securely stored onto the IOTA ledger with authenticity. Also saving energy consumption and cost
- The technology can also be used for tracking recyclable assets within an industry, again from a cost benefit perspective
- IOTA has released a recent whitepaper which states of getting rid of the network’s most centralized component- the Coordinator. The plan more commonly known as the ‘Coordicide’ will ensure the security without the presence of a central entity and improved scalability
- Although there are many ways the IoT helps in optimizing manufacturing like inventory control, the significant advancement is digital twins handled by IOTA for all critical equipment and tools like communication of calibrated data to the Tangle to further build upon the data
- With “everything as a service” business model taking a front seat and most of them having the capabilities to 3D print titanium parts and tools, the printing data can be provided through an IOTA data marketplace
In short, companies can connect and control all their products based on IOTA (Ref. a topic of Industry 4.0) and this is a real alternative to cloud solutions. In manufacturing, the key aspect to a digitalized system and adoption of Industry 4.0 is driving a machine-to-machine conversation. In addition to this the future of IoT will continue along these lines with more data-driven business models requiring a digital ledger. IOTA may come to the rescue in these torrid times at the industrial front.
Other articles by Title Chatterjee here.
![]() This article was written by Titli Chatterjee. She has been leading ER&D/Industry 4.0 research initiatives of NASSCOM, having experience in research and consulting in the areas of emerging technologies and engineering services. In her current role as Manager – Research, she is closely working with the industry leaders, start-ups, government and other stakeholders in formulating a roadmap in disruptive technologies for Indian IT-BPM industry and highlighting how technology can be a game changer at the industrial front.
This article was written by Titli Chatterjee. She has been leading ER&D/Industry 4.0 research initiatives of NASSCOM, having experience in research and consulting in the areas of emerging technologies and engineering services. In her current role as Manager – Research, she is closely working with the industry leaders, start-ups, government and other stakeholders in formulating a roadmap in disruptive technologies for Indian IT-BPM industry and highlighting how technology can be a game changer at the industrial front.
Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.


Pingback: Enabling Manufacturing using IOTA – A possible approach post Covid-19 paradigm – IoT – Internet of Things