Virtual power plants: distributed generation is not a threat, it’s an opportunity
Almost 60 percent of utility executives in 20 countries rank distributed generation as the biggest disrupter to their operations, according to a 2017 survey by Accenture, the global services company. Distributed generation, the executives predict, will reduce their revenues, increase grid faults and erode their business models.
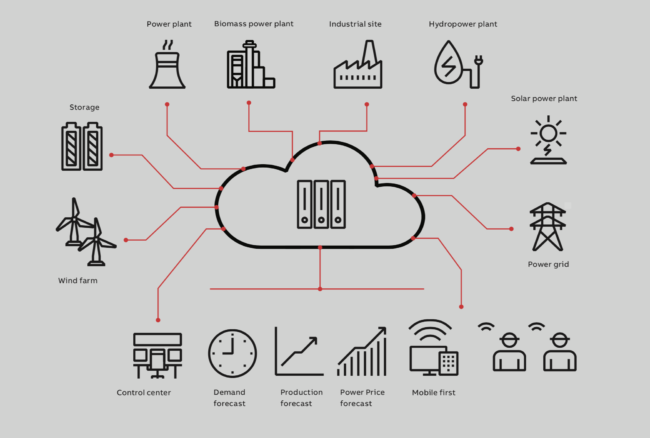
But is distributed generation a threat or an opportunity? Virtual power plants, also known as virtual power pools, are a proven way to harness the advantages of multi-unit distributed generation. They do so across an impressive range of applications which enable:
- utilities and distributed energy companies to seamlessly integrate, optimize and trade production from thousands of small-scale generators across large geographic areas;
- municipal utilities to balance production with consumption in diverse, multi-source energy systems by utilizing day-ahead and intra-day planning;
- microgrids to integrate more renewables and minimize their use of costly, CO2-emitting fossil fuel, without risk to grid stability and reliability;
- industries to cut their energy costs by 5-10 percent without impacting production volumes and delivery commitments; and
- conventional multi-unit power plants to optimize production and respond quickly and flexibly to market requirements by operating internally as a virtual power pool.
Read more about AI enabled Plant Optimization
Virtual power plants/pools (VPP), are fast becoming a driving force in the power industry, due to rising demand for energy and the global turn to renewables.
Check out some of the startups we spotted at Web Summit this year, focused on clean energy and renewable energy.
By 2025 there will be 1 billion more people on the planet, all requiring electricity. And by 2040, 60 percent of the power generated worldwide will come from renewable sources, almost half of which will be from wind and solar photovoltaic. Much of this solar and wind power will be generated by small-scale producers – homes, businesses and municipalities.
As a result, the need is escalating for virtual power plants that combine multiple, geographically dispersed generation units into a single optimized entity that can plan and adjust production dynamically and trade intelligently on the energy market.
Further reading: Are We Doing Enough to Secure the US Power Grid?
Download this free thought leadership whitepaper and you will find out more about:
- Microgrids
- Business models and energy trading
- The digital building blocks of a VPP
Also, the whitepaper contains five use cases, all of these being ABB solutions.
This is an excerpt of the Virtual power plants thought leadership white paper. More resources about power generation and water industries on ABB’s website.