Flexibility, ingrained security and centralized management are the touchstone of successful network deployments in just about any setting, especially as devices and services proliferate whether it be over wired or wireless infrastructure.
What Free-Use Wireless Spectrum Delivers
A lot has been coming together for 2021. The advent of 5G over CBRS “free-to-use spectrum,” edge cloud and mature open source SDN platforms is the trifecta that can and will deliver the desired benefits that manufacturers need, and help fulfill what is widely known as the Industry 4.0 revolution and associated Industrial Internet of Things (IIOT) Projects.
In fact, research advisory firm Gartner reports that by 2025, half or more of enterprise applications in production will be IoT ready, requiring robust and reliable connectivity to the enterprise apps. Additionally, IDC’s FutureScape report notes that a clear “70% majority of IoT deployments by 2023 will include edge-based decision making to support organizations’ operational and strategic agendas, requiring edge processing.
Reliable connectivity, secure data management and pervasive process automation have played a pivotal role in the evolution of the enterprise in IoT and towards a smart digital enterprise. With the increasing use of robots, cameras and IIoT devices and wireless industrial sensors, robust, low-latency and secure wireless connectivity for mission critical applications is required by enterprises to enable new operational Wireless technology solutions for IIoT.
Existing Wi-Fi networks
Current Wi-Fi networks can lack the necessary predictability, reliability, low-latency and data security. The existing closed and bespoke private cellular solutions are too expensive and complex to deploy, and hence, still out of reach of most enterprises.
One way to solve the problem is building open source, private cellular connectivity and the 5G connected edge cloud for enterprises. This can be a catalyst for accelerating smart enterprise digital transformation with open source, software-defined cellular connectivity and tightly integrated cloud native edge compute on COTS hardware.
For several years, digital transformation of enterprise operations, aided by industrial IoT, big data analytics, AI/ML, and resulting automation and closed-loop control, has been on the top of the priority-list for most enterprise CIOs. CEOs and CIOs wish to drive favorable business outcomes by getting real-time visibility and control of their physical facilities, raw goods and infrastructure, work-in-progress and operational processes, with an eye to increase competitiveness, productivity and ROI.
Warehouses, manufacturing floors, retail, smart enterprises and represent four mission critical enterprise applications that require low-latency connectivity to infrastructure, with much higher reliability, privacy and security than offered by either Wi-Fi or national mobile operators.
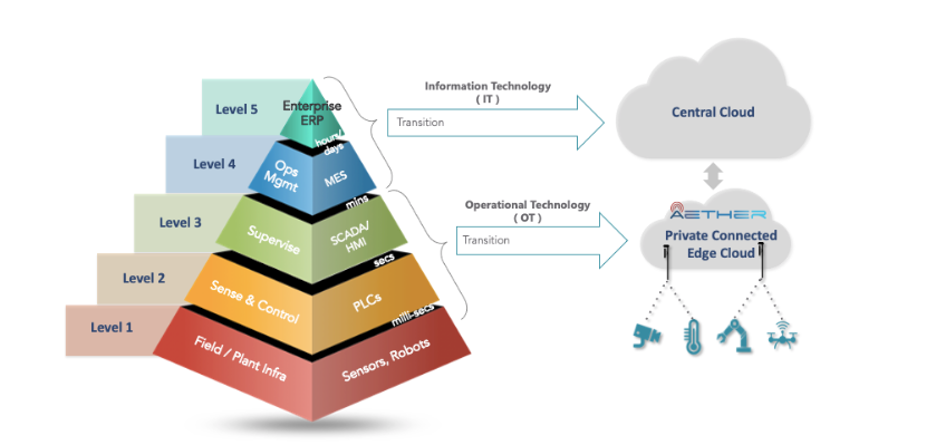
The communication and compute required for levels 1, 2 and 3 have much stricter latency constraints(sub-second). These technology components are generally termed as operational technology (OT), as opposed to the IT components like manufacturing execution system (MES) and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems.
The Automation Pyramid (fig 1) shows the communication and compute required for levels 1, 2 and 3 have much stricter latency constraints(sub-second). These mission critical technology components are generally termed as operational technology (OT), as opposed to the IT components like manufacturing execution system (MES) and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems.
Benefits of Industrial IoT with Free-Use Wireless Spectrum
Considering above, open source 5G / LTE connectivity is ideally suited to host the virtualized OT applications and platforms and offers low latency communication with QoS for these to communicate with the field/plan infrastructure. Open source can reveal technical innovations and managed service delivery model with several benefits to the enterprises:
- Assured connectivity for Mission Critical workloads: predictable and high bandwidth low-latency connectivity with quality of service guarantees for OT applications, enabled by network slicing. The edge compute workloads are highly available as a result of the self-healing orchestration of micro-services via Kubernetes
- Data sovereignty and control: Some data can’t be in the cloud and needs to stay local, either because of proximity to the source of data or the cost of shuttling the data between private infrastructure and the cloud. Another reason is sometimes due to the sensitivity of the data or regulations
- Open source enables local breakout of such critical data traffic. This allows enterprises to retain top-down programmable control of their systems and data, in turn, allowing enterprises to control their own destiny and avoid becoming locked into any single hyper-scaler’s ecosystem
- Security: Open source will comply with 5G/3GPP security standards, and hence offers end device security equivalent to a national mobile network provider. Additionally, deep traffic visibility and programmable access control offers extra layers of protection
- Improved economics: An open source software infrastructure run on COTS hardware and small cells leverages free-to-use cellular spectrum including the CBRS band in the US and dedicated licensed bands for enterprise use in Germany, and soon also in the UK, Sweden, Hong Kong and Australia
- Open source can be less costly than managed WiFi per sqare foot of coverage, but just as easily consumable.
- Ease of Wi-Fi: Open source tames the complexity of the LTE/5G standards to enable an easy-to-consume connectivity service that is as adaptable as Wi-Fi, but with all the architectural benefits and predictable performance of a 3GPP-compliant solution.
Scalable Hybrid Cloud Support: The cloud native edges can work with enterprise apps running on private or public central clouds.
About the Author
This article was written by Aseem Parikh, Vice President, Partnerships and Solutions, Open Networking Foundation.



