Harnessing the Power of the Intelligent Edge
Over the past 10 years we’ve watched cloud computing come of age as more and more companies send their data to the cloud for processing, storage, and management rather than keeping that data on a local server or Edge gateway. The benefits of cloud computing are vast, however there is another key development on the horizon as the Internet of Things matures: Edge computing.
Edge computing takes some of the essential data processing and analytics work from the cloud and brings it to the Edge devices – not replacing cloud computing, but complementing the solution. Gartner predicts that while currently only 10 percent of enterprise-generated data is processed at the Edge, by 2022 that figure will reach 50 percent. Half of all processing power is expected to slowly shift from the cloud to Edge devices, leading to IoT projects that utilize the power of both cloud computing and the intelligent Edge to make smart business decisions.
The Need for Data from the Intelligent Edge
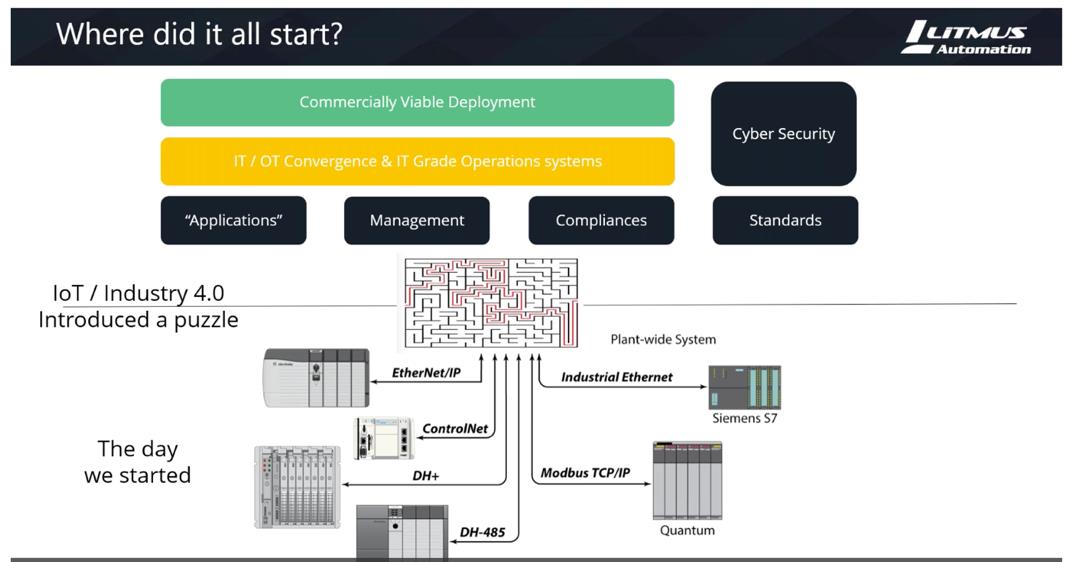
There are several trends that point to the need for harnessing the power of the intelligent Edge. First, the onset of Industry 4.0, or the “smart factory,” brought about the fundamental need in the industrial market for an IT/OT converged ecosystem. Project success is evolving to be more than just collecting vast amounts of data, and instead focuses on analyzing the data and creating value. As shown in Figure 1, Industry 4.0 has created new problems for how to manage disparate devices and legacy systems, implementing compliance and standards, security and test practices.
Artificial intelligence, or machine learning, is another key technology driver for Edge computing. Machine learning optimizes performance by quickly processing large, interconnected data sets. Depending on the application, the system is much more efficient at the Edge rather than in the cloud. For instance, consider an AI-enabled manufacturing robot that moves parts across the factory floor. If machine learning happened in the cloud, processing delays may cause safety or performance issues. Also, these manufacturing robots generate tremendous amounts of data, which would make it cost prohibitive to constantly send the data to the Cloud. In order to allow the autonomous vehicle to make decisions on the fly, the data processing must happen at the Edge.
Edge computing use cases range from the Nest to simple manufacturing projects to larger smart city or extended macro-level projects. The fundamental goal for all of these Edge computing projects is to collect data from a large amount of industrial assets, and then put that data to use immediately. The assets may be robotic systems, controllers, PLCs, or many other devices. Some of these devices are prepared for IoT, while others were never designed for IoT projects. The common thread is the challenge of gathering data from those disparate devices, then processing, analyzing and acting on the data right at the Edge of the network or device.
Industrial Use Case: Making Use of Data at the Edge
While collecting data used to be the number one concern 10 or 15 years ago, now with the introduction of the cloud and what you can do with that data as soon as you collect it is the priority. Once data is collected from various types of systems and devices in the field, the data must be pushed to multiple applications that can process and analyze the data both at the Edge and in the Cloud. The easiest way to take the next steps is with an Edge computing platform that can discover all of the devices on the network, identify them, and start collecting data within a few minutes.
These goals can be accomplished with LoopEdge and Loop from Litmus Automation. LoopEdge lets customers collect data from any type of PLC or industrial system with just a few clicks. The data coming from these industrial devices is standardized into one format and structure so that it is easily analyzed and in usable formats. Within a matter of minutes, applications can be run locally at the Edge for quick and effective processing for immediate use of this collected data. Loop is a flexible industrial IoT platform that allows customers to securely connect to the Cloud and manage any type of hardware, device, sensor or machine, while providing extensive control at scale for Edge devices, across multiple deployment sites and IoT projects.
Let’s look at a real-world use case of how LoopEdge and Loop can be used. A multinational beverage company had plants that were designed 60 years ago. Automation systems were introduced over time and some mission critical elements were designed in the 1960s and 70s. Some of the vendors were not in business anymore, and the elements obviously did not have an Edge computing philosophy in mind. Take one asset in particular – a boiler. Production line anomalies caused by old machine systems were requiring long-term and costly maintenance. The brewing process might be down for several hours when malfunctions occurred on the old machines, and the instantaneous cost of failure was $6,000 per hour.
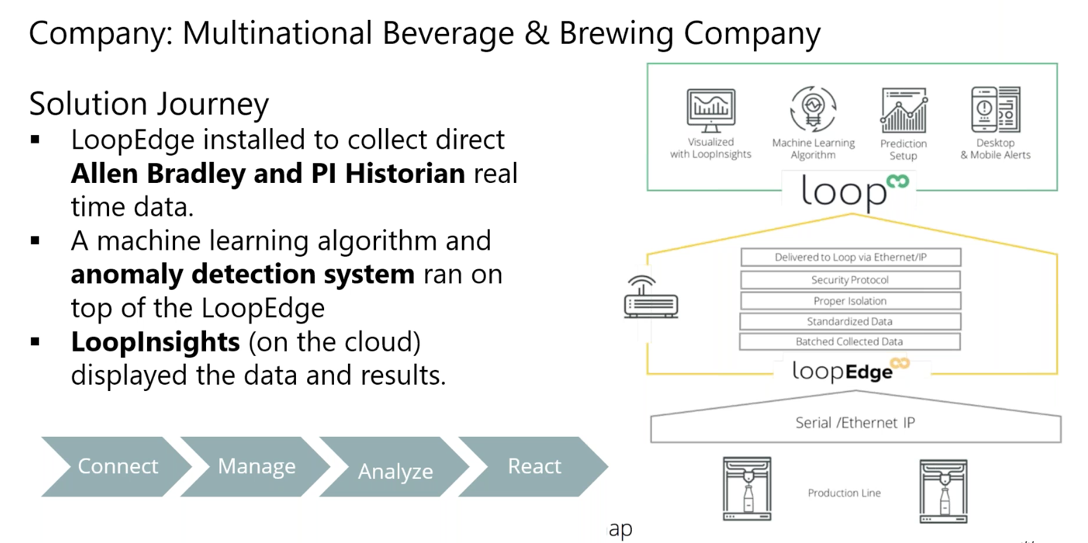
In order to avoid downtime, the beverage company adopted an Edge computing platform solution that included four key steps: connect, manage, analyze, react. LoopEdge collected real-time data directly from Allen Bradley PLCs and a PI Historian. A machine learning algorithm and model of normal behavior was created and an anomaly detection system ran on top of the collected data. Each Edge device could detect anomalies and predict pre-determined variables.
Loop connected the Edge devices and data to the cloud and a live dashboard, created on LoopInsights, for complex IoT analytics and visualization displayed the data and results. The end result within just a couple months the plant manager could receive failure prediction for the machines 9 hours in advance. Maintenance alerts were generated and a backup system was arranged.
Conclusion
The use case points out the need for industrial device connectivity enabled by a proper Edge computing framework such as LoopEdge. Some assets are prepared for IoT while others are not, and Litmus Automation created this artificial intelligence device connectivity solution to gather valuable data from any device, no matter when it was made. The Loop Edge computing marketplace has 45+ applications available such as database, next-gene analytics, machine learning, visualization and smart alerting that can quickly make use of the collected data at the Edge.
A framework helps companies get more out of their Edge computing hardware. The right framework enables the development of more applications on top of the same Edge computing system, the ability to scale the solution, and the capacity to take one small piece of hardware and extend it to multiple applications. In the end, this combination of Edge computing and cloud computing power can allow industrial customers to implement next generation IoT solutions that efficiently collect a lot of data, and process it immediately for better business decisions.
 This article was written by Vatsal Shah, Co-founder and CEO of Litmus Automation. He has extensive experience with electronics hardware design, enterprise platforms, and industrial engineering.
This article was written by Vatsal Shah, Co-founder and CEO of Litmus Automation. He has extensive experience with electronics hardware design, enterprise platforms, and industrial engineering.