What is Smart Agriculture? How can we put it Into Practice in Areas without Mobile Coverage?
Also known as Agriculture 4.0, smart agriculture is the application of information and data technologies to optimize complex agricultural systems involving individual machines and all agricultural operations.
Smart agriculture incorporates information and communication technologies into machinery, equipment and sensors used in agricultural production systems. Technologies such as IoT and cloud computing are advancing this development even further by introducing more robots and artificial intelligence to agriculture.
For example, farmers can have real-time data on the condition of their assets through IoT connectivity, and thus know, for example, the status of:
- Land quality
- Plant
- Weather
- Location of assets
- Status assets
- The use of resources
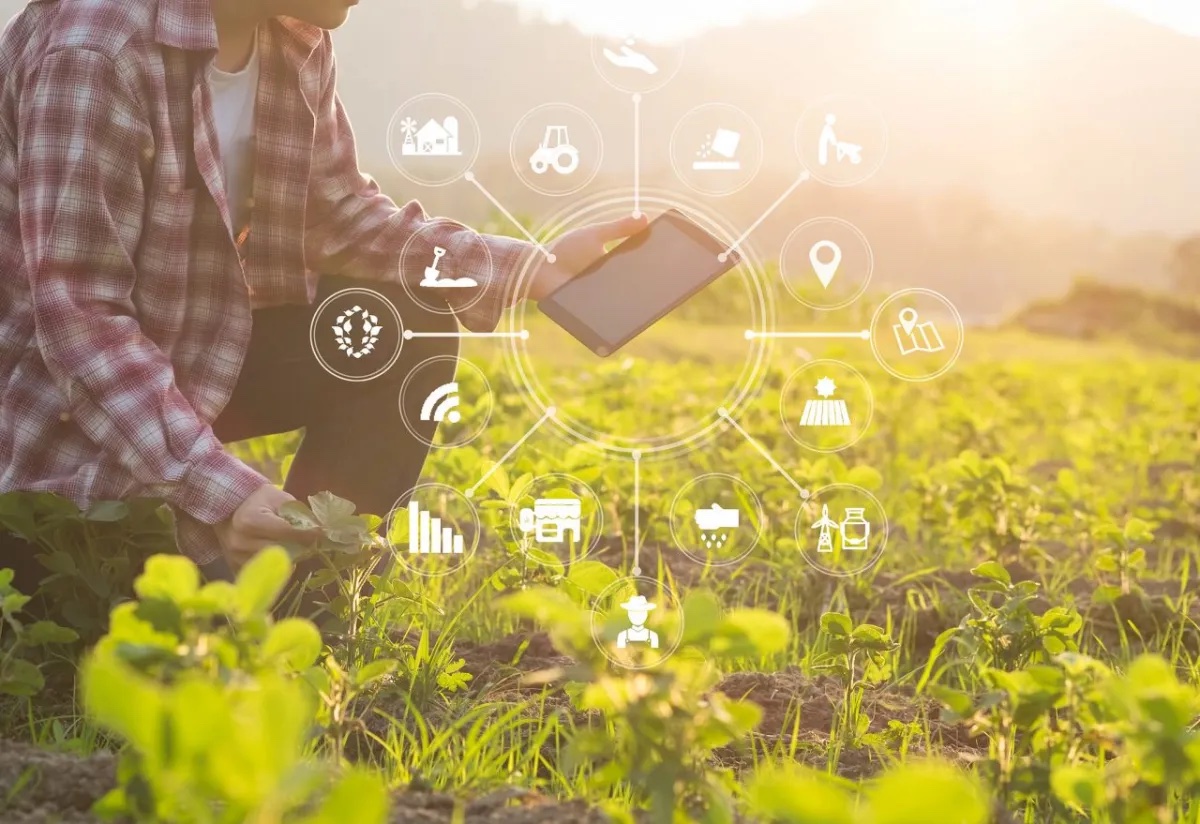

Smart agriculture practices allow the generation of a large volume of data and information. Professionals can use this information to make data-driven decisions and take the most appropriate action at the best time to improve productivity and profitability.
How does smart agriculture work?
The use of smart agricultural tools is possible thanks to the use of sensors connected to a network.
What is a sensor?
A sensor is an electrotechnical device that is located in the zone or asset that we want to parameterize. These sensors:
- Measure physical quantities from the environment
- Convert these measurements into data signals
- Signals are read and interpreted by an instrument

What can a sensor measure?
Some of the measurements read by the sensor can be:
- Temperature
- Humidity
- Light
- Pressure
- Noise
- Velocity
- Direction
- Size and weight
But how to implement smart agriculture in remote areas, where mobile connectivity does not serve?
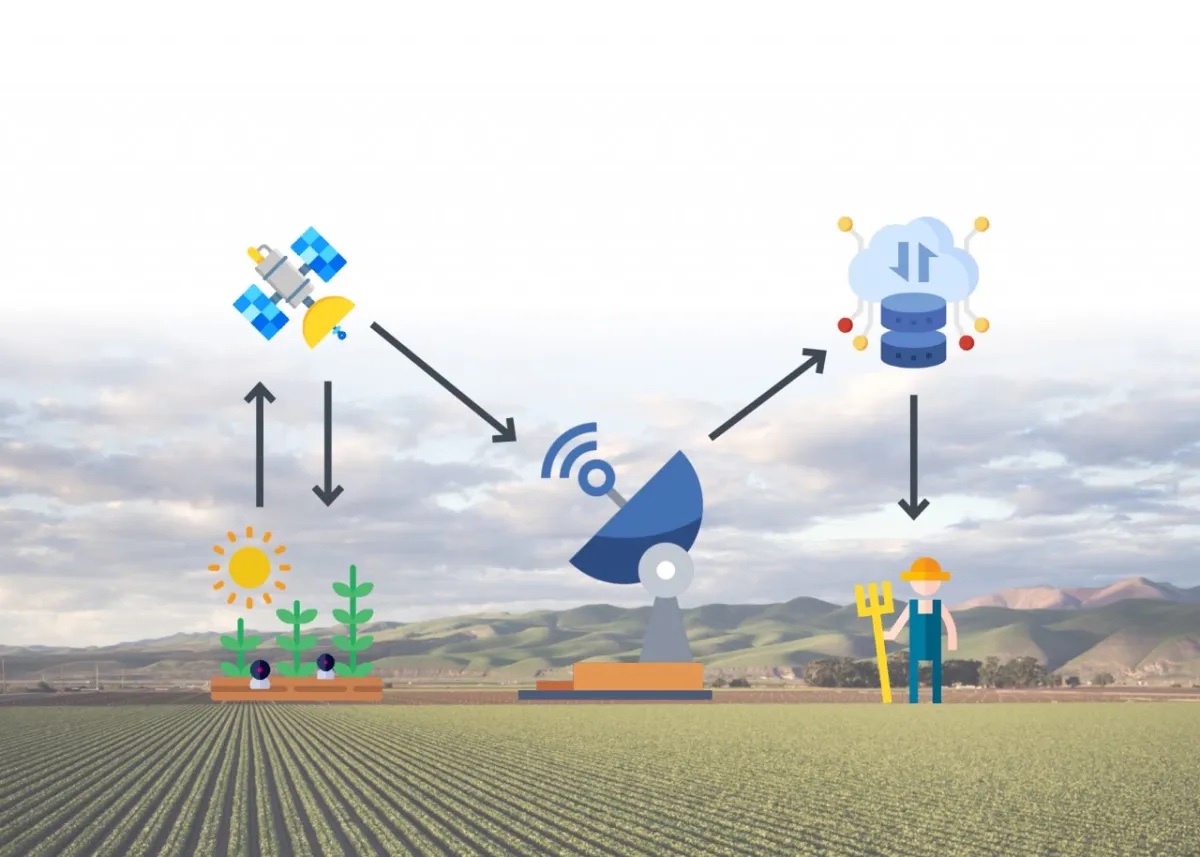
IoT connectivity via satellites
The aerospace sector is undergoing a change in its structure and its players. In recent years, start-ups, that develop new technologies to access space in a faster and cheaper way than decades ago, have appeared. Today, there are satellite platforms of highly reduced sizes (microsatellites, nanosatellites, picosatellites) that allow us to have information of these remote areas, previously mentioned, without having to assume large investments.
How? The smart sensors, distributed by the study assets, collect, encrypt, and extract the really valid information from the parameters analyzed using predictive algorithms.
These sensors send the encrypted data to the satellite platform. Subsequently, these secure and informative data are sent by the picosatellite to a ground station, where they are collected and sent to our cloud service. Here all this data is collected and stored and, through an online dashboard or through integration with API, all the information that the farmer needs to know about the status of his crop is displayed.
Why do we need to implement smart agriculture?
The most “smarter” agriculture is no longer an “advanced” tactic for smart agriculturist; it is becoming an increasingly necessary way to optimize and preserve human and natural resources.
- Agricultural labor is increasingly scarce due to urban migration and an aging population.
- The intensification of climate change is altering growing conditions in less predictable ways.
- Earth’s resources and biodiversity are declining.
Smart agriculture tools can help reduce these impacts, minimize environmental constraints, and lower production costs in agricultural activities. They also introduce a new level of technology to agriculture, including mapping, robotics, geomatics, automation, decision making, and statistical processes.
That is why we should try to adopt this type of process in our productive activities, not only to improve our productivity and profitability, but also for social awareness and to preserve the resources of our planet.
More about: Smart Technology in Agriculture
About the author
This article was written by Vicente González Negro, CTO & Co-Founder at Fossa Systems and originally it was published here.
